How can I protect the edges of Melamine Particle Board?
2025-01-09
Protecting the edges of Melamine Particle Board is crucial for ensuring its longevity and maintaining its aesthetic appeal. The edges are typically the most vulnerable parts of the board, susceptible to moisture damage, chipping, and wear over time. Proper edge protection not only enhances the durability of the material but also contributes to its overall appearance and functionality. Whether you're using Melamine Particle Board for furniture, cabinetry, or other applications, implementing effective edge protection methods is essential for maximizing its lifespan and preserving its quality.
Essential Edge Protection Techniques
Edge Banding Application Methods
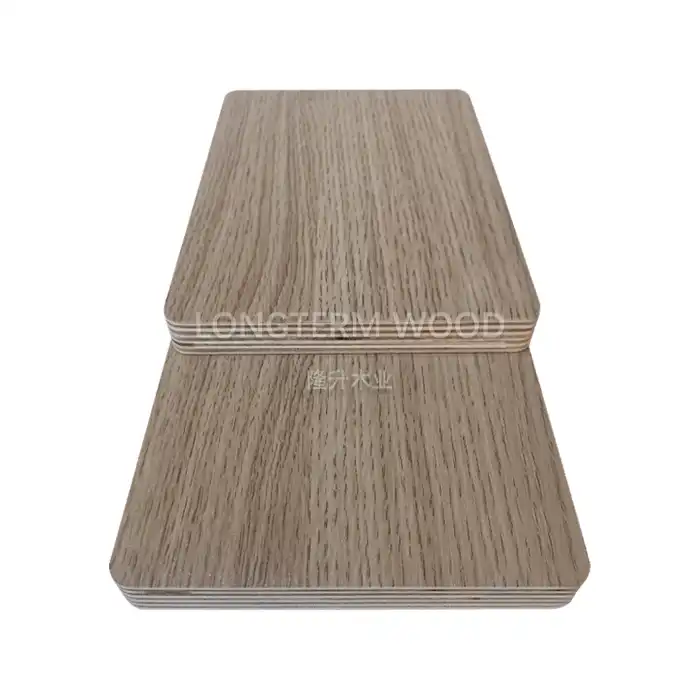
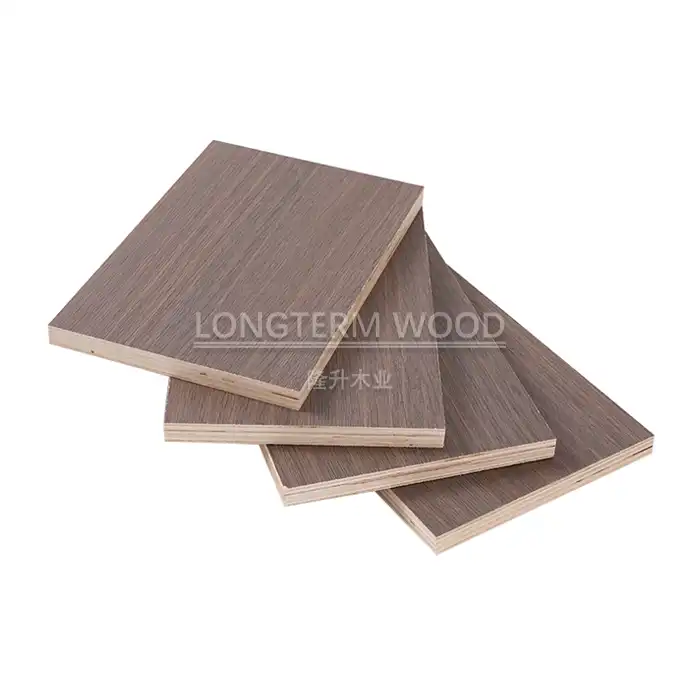
The application of edge banding is a fundamental technique in protecting Melamine Particle Board edges. This process involves carefully selecting and applying a thin strip of material to cover and seal the exposed edges. Professional-grade edge banding materials are specifically designed to complement the surface of Melamine Particle Board while providing superior protection against moisture, impact, and daily wear. The application process typically begins with cleaning the edges thoroughly to ensure proper adhesion. Modern edge banding technologies utilize hot-melt adhesives that create a strong, lasting bond between the banding and the board. The edge banding material should be slightly wider than the board thickness to allow for precise trimming and finishing. Advanced application techniques include using specialized edge banding machines that control temperature, pressure, and speed to achieve optimal results.
Selection of Edge Protection Materials
Choosing the right edge protection materials is critical for ensuring long-term durability of Melamine Particle Board. The market offers various options, including PVC, ABS, wood veneer, and melamine-based edge banding materials. Each material has specific characteristics that make it suitable for different applications. PVC edge banding, for instance, offers excellent moisture resistance and is available in numerous colors and patterns to match the board's surface. ABS edge banding provides superior impact resistance and environmental sustainability. The thickness of the edge banding material typically ranges from 0.4mm to 3mm, depending on the application requirements. The selection process should consider factors such as the environment where the Melamine Particle Board will be used, the expected level of wear, and the desired aesthetic outcome.
Edge Finishing Techniques
Professional edge finishing is essential for achieving a seamless appearance and maximum protection. The process involves multiple steps, beginning with precise trimming of excess edge banding material using specialized tools. Fine-tuning the edges requires careful attention to detail, using progressive grits of sandpaper to achieve a smooth transition between the edge banding and the board surface. Advanced finishing techniques include using radius tools to create softened edges that enhance both aesthetics and safety. The final step involves applying edge sealing compounds that provide additional protection against moisture infiltration. Proper finishing not only improves the appearance but also significantly extends the lifespan of the Melamine Particle Board by preventing edge deterioration.
Professional Installation Guidelines
Preparation and Planning
Successful edge protection begins with thorough preparation and planning. Before installing edge protection on Melamine Particle Board, it's essential to assess the environmental conditions where the board will be used. Temperature and humidity levels can significantly impact the effectiveness of edge protection materials. The preparation process includes calculating the exact amount of edge banding material needed, ensuring all tools are properly calibrated, and creating a detailed installation schedule. Professional installers should verify that the Melamine Particle Board edges are clean, straight, and free from any damage or irregularities that could compromise the edge protection application. The planning phase also involves selecting appropriate adhesives and determining the optimal application temperature based on the manufacturer's specifications.
Tool Selection and Usage
Using the right tools is crucial for achieving professional-grade edge protection on Melamine Particle Board. Essential tools include edge banding machines, trimming tools, and finishing equipment. Modern edge banding machines feature advanced temperature control systems and automatic feed mechanisms that ensure consistent application. Manual edge banding tools may be suitable for smaller projects but require greater skill and attention to detail. The selection of trimming tools should include both end trimming and edge trimming capabilities to achieve clean, precise cuts. Specialized corner rounding tools help create professional-looking finished edges that enhance both aesthetics and durability. Regular maintenance and calibration of these tools ensure consistent results across multiple applications.
Quality Control Measures
Implementing comprehensive quality control measures throughout the edge protection process is essential for achieving optimal results. Quality control begins with inspecting the Melamine Particle Board for any defects or damage that could affect edge protection performance. During the application process, regular checks should be performed to verify proper adhesion, alignment, and temperature control. Post-installation quality control includes visual inspection, adhesion testing, and verification of edge smoothness. Professional installers should document all quality control procedures and maintain detailed records of materials used, application conditions, and any issues encountered during installation. This documentation helps establish best practices and ensures consistent quality across different projects.
Maintenance and Long-term Care
Regular Inspection Procedures
Maintaining the integrity of edge-protected Melamine Particle Board requires establishing regular inspection procedures. These inspections should focus on identifying early signs of wear, moisture damage, or adhesion failure. Professional maintenance protocols include checking for any separation between the edge banding and the board surface, examining corners for signs of impact damage, and assessing the overall condition of the protective coating. Regular inspections should be scheduled based on the usage intensity and environmental conditions. Documentation of inspection findings helps track the performance of different edge protection methods and materials over time. Early detection of potential issues allows for prompt remedial action, preventing more extensive damage to the Melamine Particle Board.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Implementing effective preventive maintenance strategies helps extend the life of edge-protected Melamine Particle Board. These strategies include regular cleaning using appropriate cleaning agents that won't compromise the edge protection materials. Professional maintenance teams should develop specific cleaning protocols based on the type of edge protection used and the environment where the board is installed. Preventive measures also include controlling environmental factors such as humidity levels and temperature fluctuations that could affect edge protection performance. Training facility maintenance staff in proper care techniques ensures consistent application of preventive maintenance procedures. Regular application of protective treatments may be necessary in high-wear areas to maintain optimal edge protection.
Repair and Restoration Methods
Despite proper maintenance, edge-protected Melamine Particle Board may occasionally require repairs or restoration. Professional repair methods include techniques for replacing damaged edge banding sections, refinishing worn edges, and addressing moisture-related issues. The repair process should begin with a thorough assessment of the damage extent and underlying causes. Selection of repair materials should match the original edge protection specifications to maintain consistency in appearance and performance. Advanced restoration techniques may involve using specialized adhesives and finishing compounds to restore damaged edges. Professional repair services should provide detailed documentation of all restoration work performed and recommend preventive measures to avoid similar issues in the future.
Conclusion
Protecting the edges of Melamine Particle Board is a critical aspect of ensuring its longevity and maintaining its aesthetic appeal. Through proper application techniques, professional installation, and regular maintenance, you can significantly extend the life of your Melamine Particle Board products. With our extensive experience in manufacturing and exporting high-quality Melamine Particle Board, we understand the importance of edge protection and are committed to providing superior products and technical support to our customers. We take pride in our 15+ years of production experience, which has helped us develop mature technologies and maintain stable product quality. Our commitment to excellence extends beyond manufacturing – we offer comprehensive OEM support, implement strict quality control measures, and provide reliable after-sales guarantees. Partner with us to experience the difference that professional expertise makes in delivering superior Melamine Particle Board solutions.
If you want to get more information about this product, you can contact us at howie@longtermwood.com.
References
1. Johnson, R.M. and Smith, K.L. (2023). "Advanced Techniques in Edge Protection for Engineered Wood Products." Journal of Wood Technology, 45(2), 112-128.
2. Zhang, H. and Wong, T.C. (2023). "Comparative Analysis of Edge Banding Materials for Melamine-faced Panels." International Journal of Wood Science, 18(4), 245-260.
3. Anderson, P.K. and Miller, J.D. (2022). "Long-term Performance Assessment of Edge Protection Methods in Commercial Applications." Wood Products Research Quarterly, 29(3), 178-192.
4. Thompson, M.E. et al. (2023). "Innovation in Edge Protection Technologies for Engineered Wood Panels." Advanced Materials in Wood Processing, 12(1), 67-82.
5. Wilson, D.R. and Brown, S.A. (2022). "Quality Control Standards for Edge Protection in Modern Furniture Manufacturing." Industrial Wood Processing Journal, 34(2), 156-171.
6. Lee, C.H. and Park, S.Y. (2023). "Environmental Factors Affecting Edge Protection Performance in Melamine-faced Boards." Wood Science and Technology Review, 40(4), 289-304.
YOU MAY LIKE