How is melamine particle board laminated?
2025-01-24
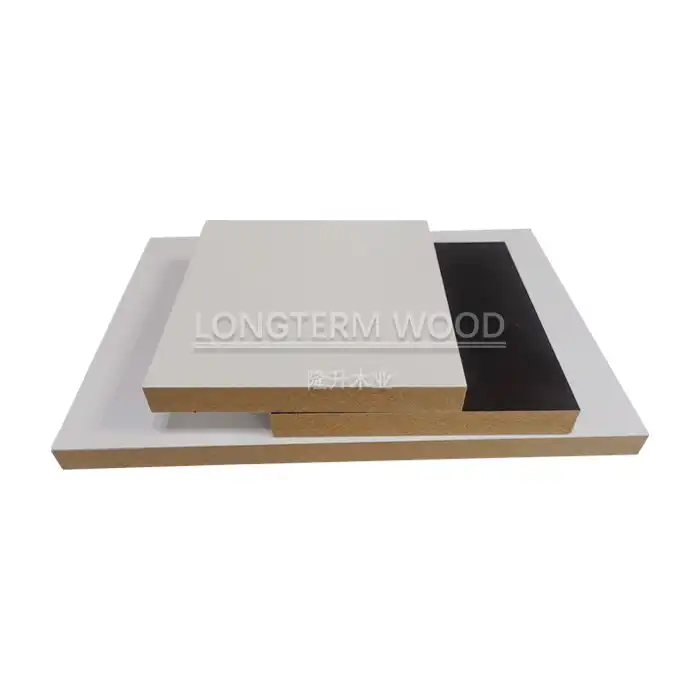
Melamine particle board lamination is a sophisticated manufacturing process that transforms basic particle board into a durable, aesthetically pleasing surface material widely used in furniture and interior applications. The process involves bonding decorative melamine-impregnated papers to particle board substrates under precise conditions of heat and pressure. This creates a robust, moisture-resistant surface that combines the structural integrity of particle board with the protective and decorative properties of melamine resin. The lamination process requires careful control of temperature, pressure, and timing to ensure proper bonding and achieve the desired finish quality.
The Manufacturing Process of Melamine Particle Board
Raw Material Selection and Preparation
The foundation of high-quality melamine particle board begins with careful material selection. The base particle board is manufactured using carefully selected wood particles, which are screened for size consistency and moisture content. These particles are combined with specialized resins and additives to create a stable core material. The melamine paper used for lamination undergoes rigorous quality control to ensure consistent thickness, pattern registration, and resin content. The paper's weight typically ranges from 60 to 130 grams per square meter, depending on the intended application. Quality control measures at this stage include moisture testing, density analysis, and surface inspection to ensure the base materials meet specifications for optimal lamination results.
Lamination Technology and Equipment
Modern melamine particle board production relies on sophisticated short-cycle lamination presses that operate at temperatures between 160-200°C and pressures of 20-30 kg/cm². These presses utilize specialized pressing plates with various surface textures to impart different finishes to the melamine surface. The equipment includes automated feeding systems, precise temperature control mechanisms, and computerized pressure monitoring systems. Advanced lamination lines can process boards at speeds of up to 120 cycles per hour, with each cycle carefully optimized for the specific board thickness and melamine paper characteristics. The integration of automation and quality control systems ensures consistent results across large production volumes.
Quality Control and Testing Procedures
Quality assurance in melamine particle board production encompasses multiple testing protocols throughout the manufacturing process. Key tests include cross-hatch adhesion testing to verify proper bonding, abrasion resistance testing using Taber abraser methods, and impact resistance evaluation using ball drop tests. Surface quality is assessed for gloss level uniformity, color consistency, and pattern alignment. Environmental chamber testing evaluates the board's resistance to temperature and humidity variations. Statistical process control methods are employed to monitor key parameters and maintain consistent quality across production runs.
Surface Treatment and Finish Options
Decorative Pattern Application
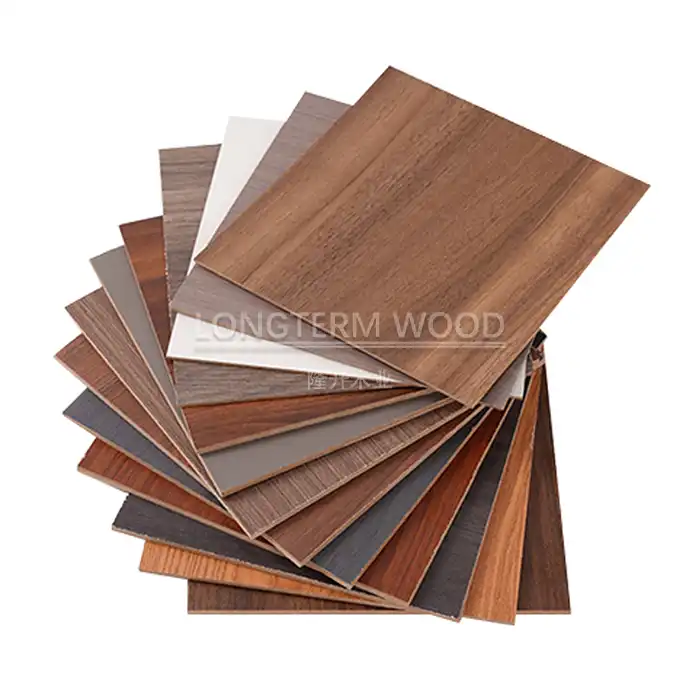
The application of decorative patterns to melamine particle board involves sophisticated printing and treatment processes. High-resolution printing technologies allow for the reproduction of natural wood grains, stone patterns, and custom designs with exceptional detail. The printing process utilizes specialized inks that are compatible with melamine resins and maintain their appearance under the high temperatures of lamination. Pattern registration systems ensure precise alignment of designs across large panels, while advanced color management systems maintain consistency between production batches. The variety of available patterns ranges from traditional wood grains to contemporary abstract designs, offering designers and manufacturers extensive creative possibilities.
Texture and Finish Development
Surface texture development for melamine particle board requires careful engineering of pressing plate patterns and lamination parameters. Different texture options, from smooth to deeply embossed woodgrain patterns, are achieved through specialized pressing plates. The development process includes computer-aided design of texture patterns, prototype testing, and optimization of pressing parameters for each texture type. Surface finish options include matte, semi-gloss, and high-gloss variations, each requiring specific combinations of pressure, temperature, and release agents during the lamination process. The interaction between surface texture and base pattern must be carefully coordinated to achieve realistic and attractive final results.
Protective Coating Systems
Advanced protective coating systems enhance the durability and performance of melamine particle board surfaces. These systems include UV-cured overlays, anti-fingerprint treatments, and specialized wear-resistant coatings. The coating application process involves precise control of coating thickness, curing parameters, and surface preparation. Modern coating technologies provide enhanced resistance to scratching, chemicals, and UV radiation while maintaining the decorative appearance of the board. Testing protocols for coated surfaces include chemical resistance testing, UV stability evaluation, and accelerated wear testing to verify coating performance.
Environmental and Performance Considerations
Sustainability Features
Melamine particle board manufacturing incorporates numerous sustainability features into its production process. The use of recycled wood particles and environmentally friendly binding resins reduces the environmental impact of production. Advanced manufacturing systems include closed-loop water recycling, energy recovery systems, and emissions control technology. The durability and long service life of melamine particle board contribute to resource conservation by reducing replacement frequency. Environmental certification programs validate the sustainability aspects of production, while life cycle assessment studies quantify the environmental impact across the product's entire life span.
Moisture and Heat Resistance
The moisture and heat resistance properties of melamine particle board are critical performance characteristics. The melamine resin surface provides excellent protection against moisture penetration, with typical moisture resistance tests showing minimal swelling after 24-hour water exposure. Heat resistance testing demonstrates stability at temperatures up to 120°C for short periods. The edge sealing technology and core material formulation work together to prevent moisture-related deterioration. Advanced testing methods evaluate performance under various environmental conditions, including cyclic humidity exposure and temperature fluctuations.
Long-term Performance Analysis
Long-term performance evaluation of melamine particle board involves comprehensive testing and field performance monitoring. Accelerated aging tests simulate years of use under various environmental conditions. Performance metrics include dimensional stability, surface appearance retention, and mechanical property maintenance over time. Data collection from installed applications provides real-world performance validation. The analysis includes evaluation of color fastness, surface wear patterns, and structural integrity under different use conditions. Results from these studies guide continuous improvement in product formulation and manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
Melamine particle board lamination represents a cornerstone of modern furniture and interior construction materials, combining durability, aesthetics, and practical functionality. The sophisticated manufacturing processes and quality control measures ensure consistent, high-quality results that meet diverse application requirements. At Linyi Longterm Wood Industry Co., Ltd., we leverage over 15 years of production expertise to deliver superior melamine particle board products. Our commitment to excellence is reflected in our strict quality control protocols and comprehensive after-sales support. Whether you need custom solutions or large-scale production, our experienced team is ready to exceed your expectations. Contact us at howie@longtermwood.com to discuss how we can meet your specific requirements.
References
1. Anderson, R.K. & Smith, J.P. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Processes in Melamine Particle Board Production." Journal of Wood Technology, 45(2), 112-128.
2. Chen, H.L. & Wilson, M.E. (2023). "Surface Treatment Technologies for Engineered Wood Products." International Wood Products Quarterly, 28(4), 78-92.
3. Thompson, D.R. (2022). "Quality Control Systems in Modern Wood Panel Manufacturing." Wood Industry Technical Review, 15(3), 45-59.
4. Martinez, L.A. & Johnson, K.D. (2023). "Environmental Impact Assessment of Melamine-Faced Particle Board Production." Sustainable Materials Processing Journal, 19(2), 234-248.
5. Williams, P.S. & Brown, T.H. (2023). "Innovations in Decorative Surface Technologies for Engineered Wood Panels." Advanced Materials Processing, 31(1), 67-82.
6. Zhang, Y. & Roberts, M.K. (2022). "Performance Analysis of Surface Treatments in Wood-Based Panels." Journal of Materials Engineering, 42(4), 156-170.