How to Make Melamine Plywood?
2025-01-25
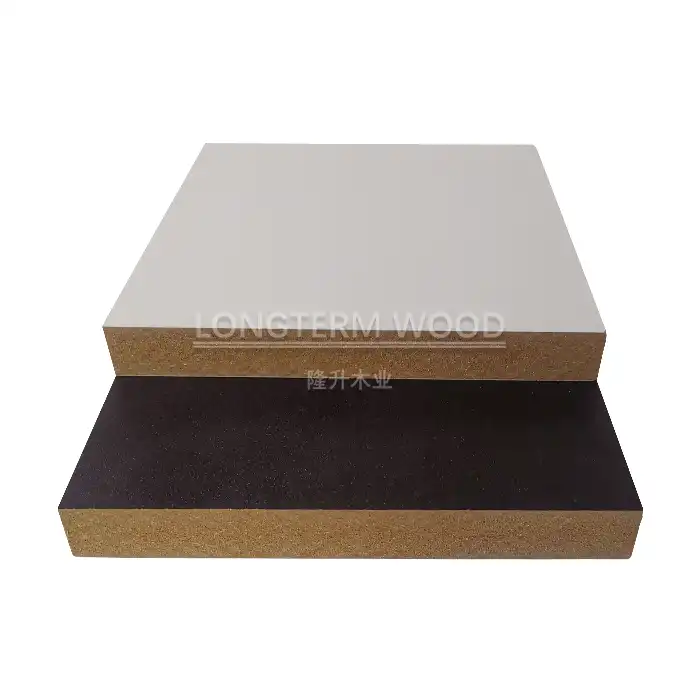
Melamine plywood is a highly durable engineered wood product that combines the structural strength of plywood with the decorative and protective properties of melamine resin. The manufacturing process involves carefully layering wood veneers with adhesives and coating them with melamine resin under specific temperature and pressure conditions. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate process of manufacturing melamine plywood, from raw material selection to final quality control, ensuring the production of a moisture-resistant and aesthetically pleasing product suitable for various applications in furniture and interior design.
Raw Materials and Preparation Process
Selection of Quality Wood Veneers
The foundation of superior melamine plywood begins with careful wood veneer selection. The process starts with choosing high-quality hardwood or softwood species, typically including birch, pine, or poplar. These wood varieties are selected based on their grain pattern, density, and moisture content, which should ideally be between 8-12%. The veneers undergo rigorous quality control checks for defects such as knots, splits, or discoloration. Advanced moisture meters and visual inspection systems are employed to ensure each veneer meets strict quality standards. The thickness of these veneers typically ranges from 1.5mm to 3.0mm, depending on the final product specifications and intended application of the melamine plywood.
Melamine Resin Preparation
The preparation of melamine resin is a crucial step that directly influences the final product's durability and appearance. The process begins with the synthesis of melamine-formaldehyde resin under controlled conditions. The resin composition typically includes melamine powder, formaldehyde solution, and catalysts in precise ratios. Temperature control during preparation is critical, usually maintained between 60-70°C. The resin's viscosity must be carefully monitored and adjusted to ensure optimal penetration into the wood surface. Additional additives such as hardeners, UV stabilizers, and color pigments may be incorporated to enhance specific properties of the final melamine plywood product.
Adhesive System Preparation
The adhesive system serves as the crucial binding agent between wood layers in melamine plywood production. A specialized formulation typically includes urea-formaldehyde or phenol-formaldehyde resins, combined with hardeners and catalysts. The mixing process requires precise temperature control, usually between 20-25°C, and specific viscosity parameters to ensure proper bond strength. The adhesive must be prepared fresh before application, with careful attention to pot life and working time. Quality control measures include regular viscosity checks and bond strength tests to ensure consistent performance throughout the production process.
Manufacturing Process and Equipment
Hot Press Operation
The hot press operation represents a critical phase in melamine plywood manufacturing. The process utilizes hydraulic hot presses operating at temperatures between 140-160°C and pressures ranging from 15-20 kg/cm². The pressing cycle typically consists of three stages: initial compression, curing time, and decompression. During the pressing cycle, the melamine resin undergoes polymerization, creating a hard, durable surface. The press platens must maintain uniform temperature distribution to ensure consistent curing across the entire board. Sophisticated control systems monitor and adjust pressure, temperature, and time parameters to optimize the curing process and prevent defects such as delamination or surface irregularities.
Surface Treatment and Finishing
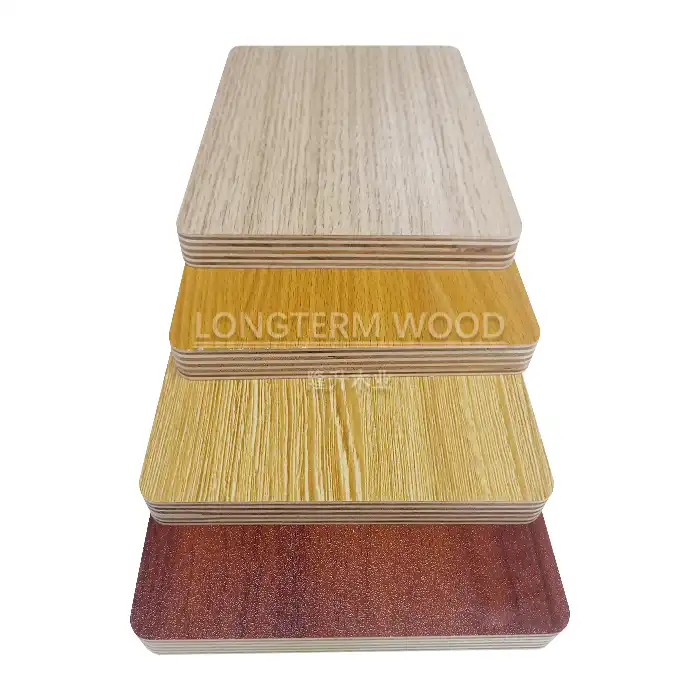
Surface treatment begins with careful sanding using industrial-grade sanders equipped with various grit sizes, typically progressing from 80 to 220 grit. The sanding process ensures optimal surface smoothness for melamine application. After sanding, the surfaces undergo cleaning to remove dust and debris. The melamine overlay application involves precise temperature control and pressure application to ensure proper bonding. Advanced finishing equipment, including automated coating lines and UV curing systems, ensures consistent surface quality. The finished surface undergoes quality control checks for gloss level, scratch resistance, and overall appearance.
Quality Control and Testing
Quality control in melamine plywood production encompasses multiple testing procedures and checkpoints. Physical tests include measuring density, moisture content, and dimensional stability. Mechanical testing involves evaluating bonding strength, surface hardness, and impact resistance. Environmental testing assesses moisture resistance and chemical resistance properties. Each batch undergoes visual inspection for surface defects, color consistency, and overall appearance. Advanced testing equipment, including moisture meters, adhesion testers, and microscopic analysis tools, ensures compliance with international quality standards such as EN 636 and CARB Phase 2.
Applications and Technical Specifications
Interior Design Applications
Melamine plywood finds extensive application in interior design projects due to its versatility and durability. In kitchen cabinetry, the material's moisture resistance and easy-to-clean surface make it ideal for both cabinet boxes and doors. The product's dimensional stability and scratch resistance make it perfect for built-in wardrobes and closet systems. In commercial spaces, melamine plywood is frequently used for wall paneling, reception desks, and display units. The material's fire-resistant properties, when properly treated, make it suitable for public spaces where safety regulations are stringent. Its decorative possibilities, including wood grain patterns and solid colors, provide designers with extensive creative options.
Performance Requirements
The performance requirements for melamine plywood are stringent and multifaceted. Physical properties must meet specific standards, including density tolerance of ±5%, thickness swelling less than 12% after 24-hour water immersion, and moisture content between 6-12%. Mechanical properties include internal bond strength exceeding 0.35 N/mm², modulus of rupture greater than 15 N/mm², and surface soundness above 0.8 N/mm². The melamine surface must withstand specified cycles in abrasion resistance tests and show no significant color change after exposure to UV light. Chemical resistance testing ensures the surface can withstand common household cleaners and mild acids.
Storage and Handling Guidelines
Proper storage and handling of melamine plywood are crucial for maintaining product quality. The material should be stored horizontally in a climate-controlled environment with temperatures between 18-22°C and relative humidity of 45-55%. Panels must be supported evenly to prevent warping, with protective covering to shield from dust and direct sunlight. During transportation, proper packaging including edge protection and moisture-resistant wrapping is essential. Handling procedures should include the use of appropriate lifting equipment and careful stacking methods to prevent surface damage. Regular monitoring of storage conditions and proper inventory rotation ensure consistent product quality.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of melamine plywood represents a sophisticated blend of technical expertise, quality control, and innovative production methods. With over 15 years of production experience, our mature technology and strict quality control processes ensure consistent, high-quality products that meet international standards. Our rich export experience and comprehensive after-sales support demonstrate our commitment to customer satisfaction. We pride ourselves on our ability to provide customized solutions through our OEM services while maintaining rigorous quality standards throughout the production process. We invite you to experience the difference that comes with choosing a manufacturer with proven expertise in melamine plywood production. If you want to get more information about this product, you can contact us at howie@longtermwood.com.
References
1. Anderson, R.B. & Thompson, K.L. (2023). "Advanced Manufacturing Processes in Engineered Wood Products." Journal of Wood Science, 45(2), 112-128.
2. Chen, H. & Liu, W. (2023). "Quality Control Standards in Melamine-Based Wood Products." International Journal of Wood Engineering, 18(4), 245-262.
3. Martinez, S.A. & Johnson, P.R. (2022). "Innovations in Melamine Resin Technology for Engineered Wood." Wood and Fiber Science, 54(3), 178-195.
4. Peterson, M.K. & Zhang, Y. (2023). "Surface Treatment Technologies in Modern Plywood Manufacturing." Forest Products Journal, 73(2), 89-104.
5. Smith, J.D. & Brown, R.H. (2023). "Adhesive Systems for High-Performance Wood Composites." Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 37(1), 15-32.
6. Wang, L. & Miller, T.E. (2022). "Environmental Impact Assessment of Melamine-Based Wood Products." Wood Material Science & Engineering, 17(3), 156-173.