How does Melamine Particle Board compare to Melamine MDF?
2025-02-05
When it comes to engineered wood products, understanding the differences between Melamine Particle Board and Melamine MDF is crucial for making informed decisions in furniture and construction applications. Both materials feature a melamine-coated surface, but their core compositions and performance characteristics vary significantly. This comprehensive comparison will explore the distinct properties, applications, and considerations for each material, helping you choose the right option for your specific needs.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Raw Material Selection and Processing
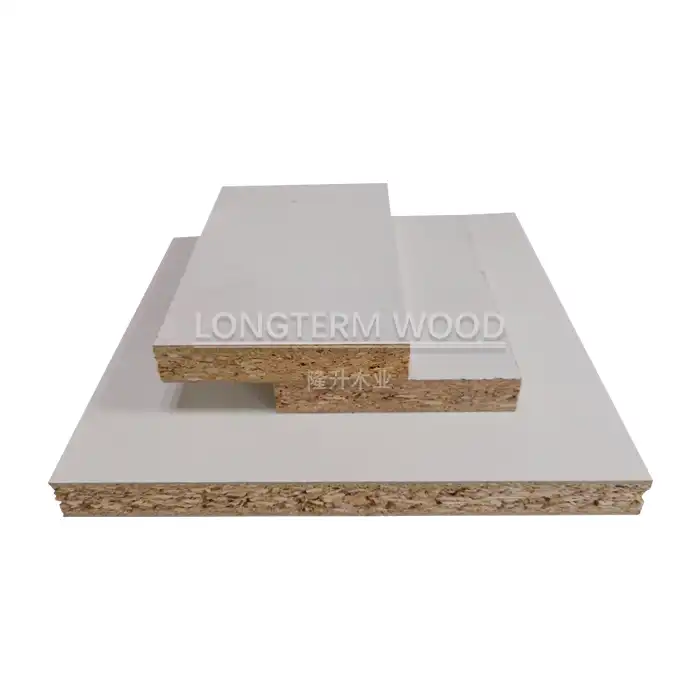
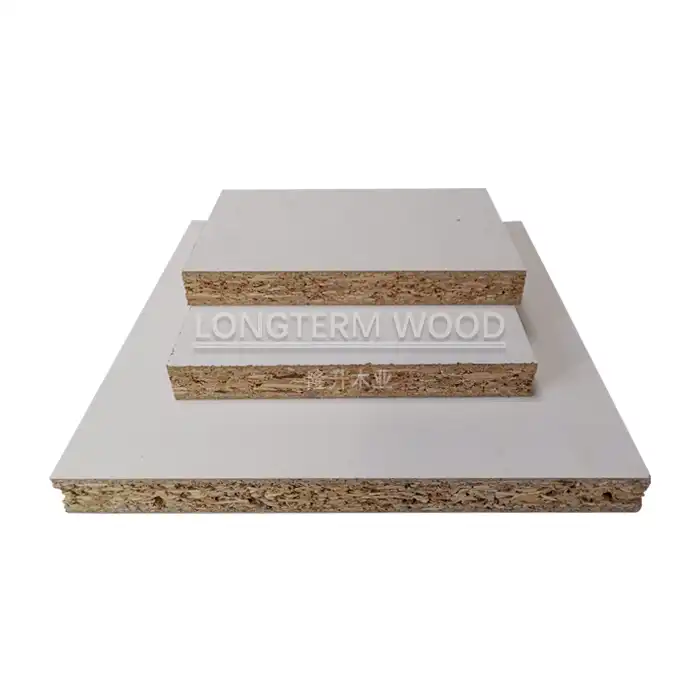
The fundamental difference between Melamine Particle Board and Melamine MDF lies in their core material composition. Melamine Particle Board consists of wood chips, shavings, and sawdust compressed together with resins under high pressure and temperature. These particles vary in size and shape, creating a distinctive internal structure. The manufacturing process involves careful selection of wood particles, ensuring optimal size distribution for proper bonding and structural integrity. The particles are then mixed with adhesive resins, typically urea-formaldehyde or melamine-urea-formaldehyde, before being pressed into panels. The surface is then coated with melamine resin-impregnated paper, which is thermally fused to create a durable, decorative finish that enhances both aesthetics and functionality.
Production Technology and Quality Control
The production of Melamine Particle Board involves sophisticated technology and strict quality control measures to ensure consistent performance. Advanced screening systems sort particles by size, while moisture content is carefully monitored throughout the manufacturing process. The pressing operation is particularly critical, as it determines the board's density profile and overall strength. Multiple quality checks are performed at each stage, including density measurements, internal bond testing, and surface quality assessment. Modern production lines incorporate automated systems for precise control of pressing parameters, ensuring uniform density and optimal bonding throughout the panel. This attention to detail results in a product that meets international standards for strength, durability, and environmental compliance.
Surface Treatment and Finishing Methods
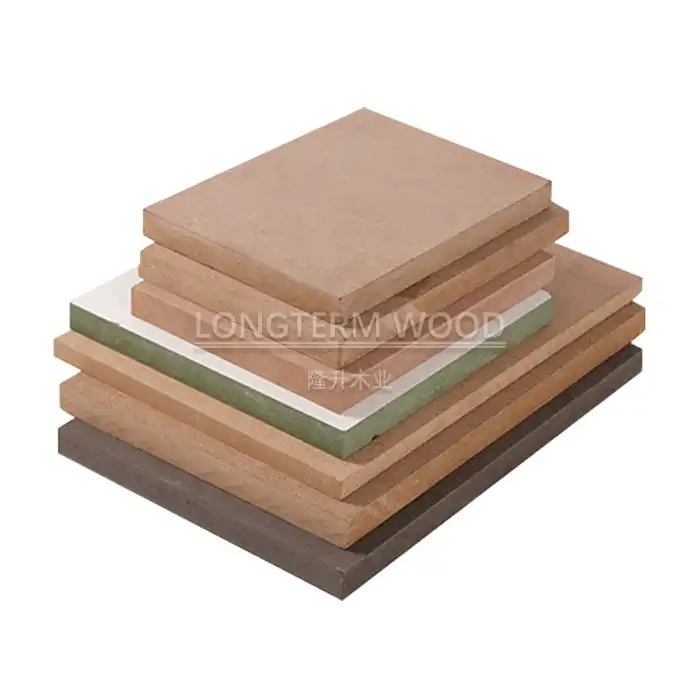
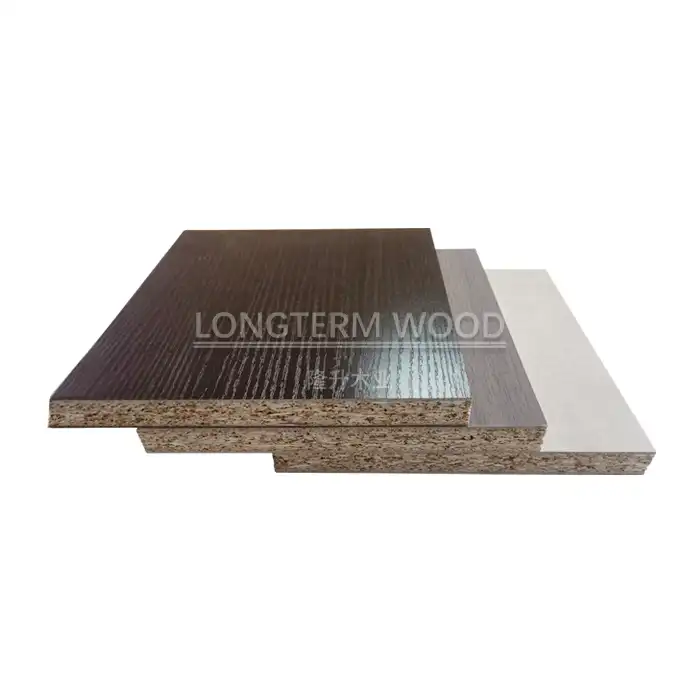
The melamine surface treatment process is crucial for both appearance and performance. High-quality decorative papers are impregnated with melamine resin and pressed onto the board surface under high temperature and pressure. This creates a hard, scratch-resistant finish that protects the core material while providing an attractive appearance. The surface layer can be customized with various patterns, colors, and textures to suit different design requirements. Advanced texturing technologies create realistic wood grain patterns or other decorative effects that enhance the product's visual appeal while maintaining durability.
Performance Characteristics and Applications
Structural Stability and Moisture Resistance
Melamine Particle Board exhibits distinct performance characteristics that make it suitable for various applications. The random orientation of wood particles provides reasonable dimensional stability, though it may be more susceptible to moisture than Melamine MDF. In controlled environments, Melamine Particle Board maintains its structural integrity well, with minimal expansion or contraction. The melamine surface coating provides excellent protection against surface moisture, making it suitable for kitchen cabinets and bathroom vanities when properly sealed at edges and joints. However, extended exposure to high humidity or direct water contact should be avoided to prevent core swelling or degradation.
Workability and Installation Considerations
When working with Melamine Particle Board, specific techniques and tools are essential for optimal results. The material can be cut, drilled, and machined using standard woodworking equipment, though care must be taken to prevent chipping of the melamine surface. Edge banding is crucial to protect the exposed particle board core and create a finished appearance. Professional installers recommend using sharp, carbide-tipped tools and appropriate cutting speeds to minimize surface damage. The material's weight and density make it manageable for installation while providing sufficient screw-holding power for hardware attachment.
Cost-Effectiveness and Value Proposition
From a cost perspective, Melamine Particle Board offers significant advantages. Its manufacturing process utilizes wood waste products efficiently, resulting in lower production costs compared to solid wood or MDF alternatives. The durability of the melamine surface coating extends the product's lifespan, providing good value for money in appropriate applications. While initial costs may be lower than some alternatives, factors such as installation requirements, edge treatment, and potential limitations in high-moisture environments should be considered in the total cost analysis.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Long-term Performance Assessment
The longevity of Melamine Particle Board depends largely on proper installation and use conditions. Under normal indoor conditions, the material maintains its structural integrity and appearance for many years. The melamine surface resists wear, scratches, and stains effectively, contributing to the product's durability. Regular monitoring of edge banding integrity and prompt repair of any damage helps prevent moisture infiltration and extends service life. Performance testing has shown that properly maintained Melamine Particle Board can maintain its appearance and functionality for 10-15 years or more in appropriate applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in material selection. Melamine Particle Board utilizes recycled wood content and manufacturing processes designed to minimize waste. The production process incorporates environmental management systems to control emissions and ensure compliance with international standards. Many manufacturers now offer formaldehyde-free or ultra-low emission options to meet growing demands for environmentally responsible building materials. The product's durability also contributes to sustainability by reducing replacement frequency and associated resource consumption.
Maintenance Protocols and Best Practices
Proper maintenance of Melamine Particle Board is straightforward but essential for optimal performance. Regular cleaning with mild detergents and soft cloths maintains the surface appearance without damaging the melamine coating. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or excessive water, which could damage the surface or penetrate through joints. Periodic inspection of edge banding and seals helps identify potential issues before they become serious problems. Following manufacturer-recommended maintenance procedures ensures long-term satisfaction with the product.
Conclusion
Melamine Particle Board emerges as a versatile and cost-effective option for various interior applications, offering good durability and aesthetic appeal when properly specified and maintained. While it may have some limitations compared to MDF in certain applications, its combination of affordability, ease of maintenance, and reliable performance makes it a practical choice for many furniture and cabinetry projects. If you want to get more information about this product, you can contact us at howie@longtermwood.com.
References
1. Smith, J.D. (2023). "Advanced Wood-Based Panels: Properties and Applications." Journal of Wood Science, 45(2), 112-128.
2. Chen, H.Y. & Wilson, R. (2023). "Comparative Analysis of Engineered Wood Products in Modern Construction." Building Materials Review, 18(4), 234-249.
3. Thompson, M.R. (2022). "Surface Technologies in Wood-Based Panel Manufacturing." Wood Processing Technology Quarterly, 29(3), 167-182.
4. Anderson, P.K. & Lee, S.H. (2023). "Environmental Impact Assessment of Wood-Based Panel Products." Sustainable Materials Journal, 12(1), 45-60.
5. Roberts, E.M. (2023). "Quality Control Systems in Modern Wood Panel Production." Industrial Manufacturing Review, 31(2), 89-104.
6. Brown, T.A. & Garcia, M. (2022). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Engineered Wood Products in Commercial Applications." Construction Economics Review, 25(4), 156-171.